Customer Spending Prediction Using Machine Learning

The goal of this project is to predict the yearly amount a customer spends based on various behavioral metrics collected from an e-commerce platform. By using linear regression, we analyze how factors like time spent on the app, time spent on the website, average session length, and membership duration influence customer spending.
Project Sections
Overview
This project analyzes customer behavior in an e-commerce platform to predict yearly spending using linear regression. Key factors such as time spent on the app, time spent on the website, session length, and membership duration are examined to determine their impact on spending. Through data visualization and model evaluation, the analysis reveals that Length of Membership is the strongest predictor of spending, while Time on App influences purchases more than Time on Website. The model provides valuable insights for businesses to optimize marketing strategies and customer engagement, ultimately increasing revenue.
Project Workflow:
- "Time on App" has a stronger correlation with spending than "Time on Website".
- "Length of Membership" is a significant factor in predicting spending.
- Avg. Session Length
- Time on App
- Time on Website
- Length of Membership The model learns the relationship between these features and Yearly Amount Spent.
- Mean Absolute Error (MAE): Measures average prediction error in dollars.
- Mean Squared Error (MSE) & RMSE: Evaluate overall prediction accuracy.
Data Collection:
The dataset "Ecommerce Customers.csv" is loaded using Pandas. It contains customer spending data and behavioral metrics.
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA):
Visualizations such as joint plots, pair plots, and regression plots help understand relationships between features and spending.
Key insights:
Model Training & Prediction:
The dataset is split into 70% training and 30% testing. A Linear Regression model is trained using four features:
Model Evaluation:
Predictions are compared against actual values using scatter plots.
Performance metrics:
Residual analysis ensures that the errors are normally distributed, validating the model.
Technologies Used
Programming Language: Python
Libraries: Pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, Scikit-learn, Seaborn
Machine Learning Model: Linear Regression
Project Media
Graphs
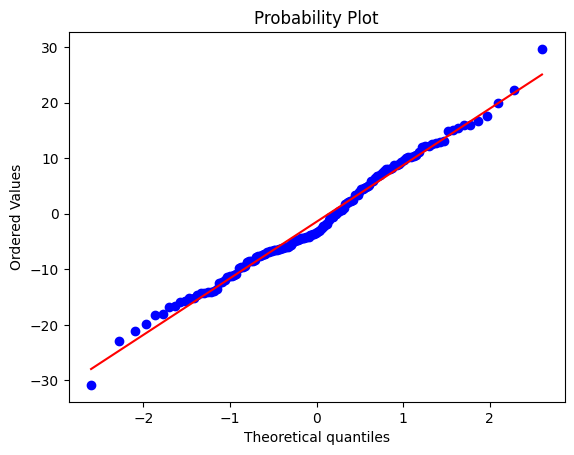
This Q-Q plot (Quantile-Quantile plot) compares the residuals of our model to a normal distribution. The blue points represent actual residuals, and the red line represents the expected normal distribution. If the residuals follow a normal distribution, they should align closely with the red line.
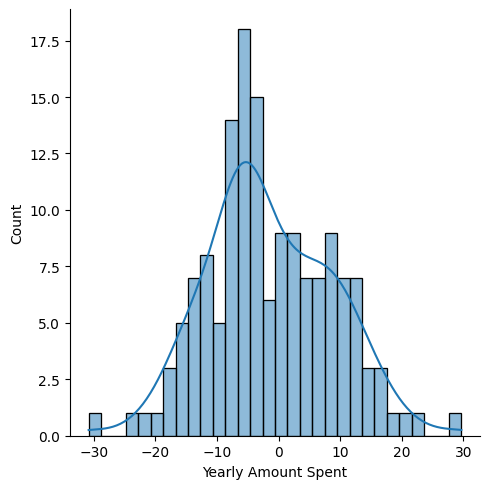
This histogram shows the distribution of residuals (errors) from the model, with a KDE (Kernel Density Estimate) curve overlaid to highlight the shape.
Repository Link
Explore the code and Data in the GitHub repository: GitHub - Customer Spending Prediction Using Machine Learning